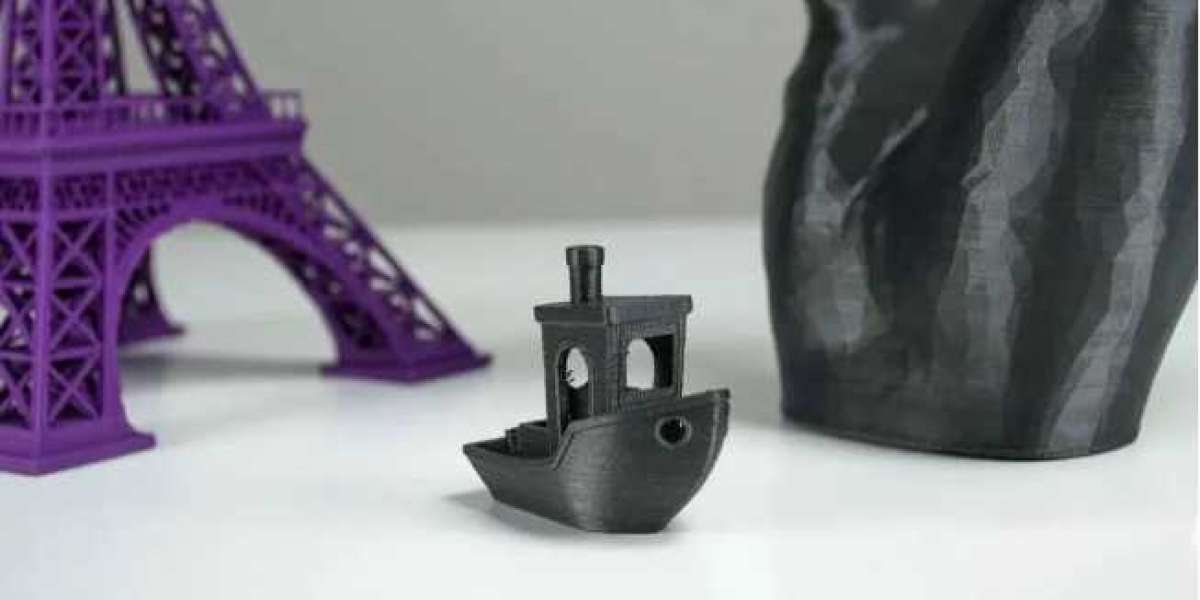
Choosing the right 3D printing filament is crucial for achieving high-quality results in your prints. With thousands of materials available, each with its own unique properties, it can be overwhelming to decide which one to use. In this guide, I’ll walk you through eight popular 3D printing filaments and what makes each one special.
When diving into the world of 3D printing, you'll quickly find that the choice of filament plays a significant role in the quality and functionality of your prints. As someone who frequently works with these materials, I can tell you that each filament has its own set of characteristics and best-use scenarios. Here’s a rundown of eight common types of 3D printing filaments:
PLA: The All-Rounder
PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is one of the most popular and widely used filaments. It’s easy to find, budget-friendly, and user-friendly, making it compatible with most FDM 3D printers. Made from renewable resources, PLA is almost odorless and one of the least harmful materials to the environment.
PETG: The Food-Safe Choice
PETG, which stands for Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified, is a step up from basic PET. The “G” in PETG means it’s modified with glycol, making the filament clearer, less brittle, and easier to print with. It offers better mechanical properties than PLA, including greater strength and flexibility.
ABS: The Tough Material
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is known for its durability and strength. Made from petroleum, ABS is frequently used in injection molding and is renowned for its toughness, heat resistance, and overall sturdiness.
TPU, TPE, TPC: The Flexible Filaments
TPEs, or Thermoplastic Elastomers, are a blend of plastic and rubber. This category includes TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), TPC (Thermoplastic Copolyester), and similar materials. TPU has been a go-to choice for flexible prints due to its excellent elasticity and resilience.
PA: The Durable Workhorse
PA, or Polyamide, is one of the most durable 3D printing materials available. It’s celebrated for its toughness, high-temperature resistance, impact resistance, and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of demanding applications.
ASA: The UV-Resistant Option
ASA, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, is known for its high impact strength and chemical resistance. It has quickly become a favorite in the 3D printing community for outdoor applications due to its resistance to UV light and weathering.
PVB: The Smooth Finisher
PVB, or Polyvinyl Butyral, is a unique filament that can be smoothed with isopropanol, unlike ABS, which requires acetone for finishing. This property makes PVB an excellent choice for achieving a smooth surface finish on printed objects.
Wood Composite Filament
Wood composite filaments are a blend of PLA with wood fibers, such as pine, birch, cedar, ebony, and willow. These filaments offer a wood-like finish and texture, giving your prints a unique, natural appearance.
Choosing the right filament depends on several factors:
Material Properties: Strength, flexibility, heat resistance, etc. Application: Whether the print is for outdoor use, food contact, etc. Printer Compatibility: Make sure the filament works with your FDM or SLA printer. Post-Processing Needs: Consider if you’ll need additional finishing like steam smoothing or injection molding. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each filament can help you select the best one for your 3D printing projects, ensuring high-quality and functional results.